What Is Kamut And What Are Its Properties?
Kamut is a cereal that was grown in Africa for many years and is gradually entering the Western diet. This is due to the benefits it brings to health and the amount of nutrients it has. It is a very attractive option to replace wheat.
It should be noted that the position of experts regarding the consumption of many cereals has changed. Certain foods such as wheat are no longer considered of good quality, due to their high degree of refinement. In its place, whole grain varieties with no added sugars are gaining ground, including kamut.
Differences between kamut and common wheat
Kamut and wheat share certain uses. Both can be the main ingredient in pasta. However, the differences are notable, the former being a much larger grain cereal, albeit with easier digestion.
One of the main differences between the two is that kamut has a higher protein content, touching 15 grams of protein per 100 grams of product. It should be remembered that these nutrients are essential to ensure proper muscle health, as stated by research published in the journal Nutrients .
At the same time, it contains a greater amount of vitamins, notably vitamin A. This substance has been shown to have a positive impact on visual health, reducing the risk of developing macular pathologies.
As far as carbohydrate intake is concerned, wheat and kamut do not present significant differences, apart from the fact that kamut itself generates a lower glycemic peak. Keep in mind that wheat is usually eaten highly refined, which is not positive for blood glucose levels.

Nutritional properties of kamut
We are going to review the properties of kamut when it is introduced within the framework of a healthy and varied diet.
Provides quality energy
Carbohydrates are essential, especially in the athlete’s diet. They manage to provide the necessary energy to start the anaerobic metabolism, responsible for the execution of maximum efforts.
In the case of sedentary people, carbohydrate needs are decreased. However, these can be added to the diet without damaging health. To achieve this objective, it is necessary to establish the necessary amounts and choose those carbohydrates with a low glycemic index.
Improves intestinal health
Kamut stands out for its fiber content. This substance is essential to promote intestinal health. It is capable of preventing the development of episodes of constipation and also reduces the risk of colon cancer, according to evidence in a trial published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition .
It is worth noting the need to include both soluble and insoluble fiber in the diet. Kamut is a good source of the latter, so the contribution can be completed by other cereals such as oats, with beta glucans in their composition.
It is an antioxidant
The antioxidant capacity of kamut comes from its vitamin A content. As we mentioned, this nutrient is capable of protecting visual health, but also of fighting inflammation or the formation of free radicals.
A good supply of said micronutrient is associated, for example, with a lower risk of developing liver-type pathology. This is stated in an article published in Nutrition and Health.
Helps control cholesterol
Although we have already commented on other occasions that diet has a limited influence on serum cholesterol levels, it is true that fiber has functions when it comes to modifying the lipid profile. Kamut, in this sense, can lower total cholesterol levels, although not dramatically.
However, keep in mind that keeping your cholesterol too low is not good for your health. The myth that lipid profile alone is a good marker for cardiovascular disease is beginning to be dispelled, unless you have extremely high lipoproteins.
Improves immune function
Among the micronutrients that kamut contains, it is necessary to make a special mention of zinc. This mineral is capable of regulating the production of testosterone in men and of ensuring the proper functioning of the immune system. Ingesting adequate doses of zinc through the daily diet will reduce the risk of infectious diseases.
Anyway, despite its benefits, you should bear in mind that kamut contains gluten in its composition, so it is not suitable for people with celiac disease. It is the same as with wheat. However, it is not advisable to remove gluten from the diet unless there is a professional diagnosis and prescription.
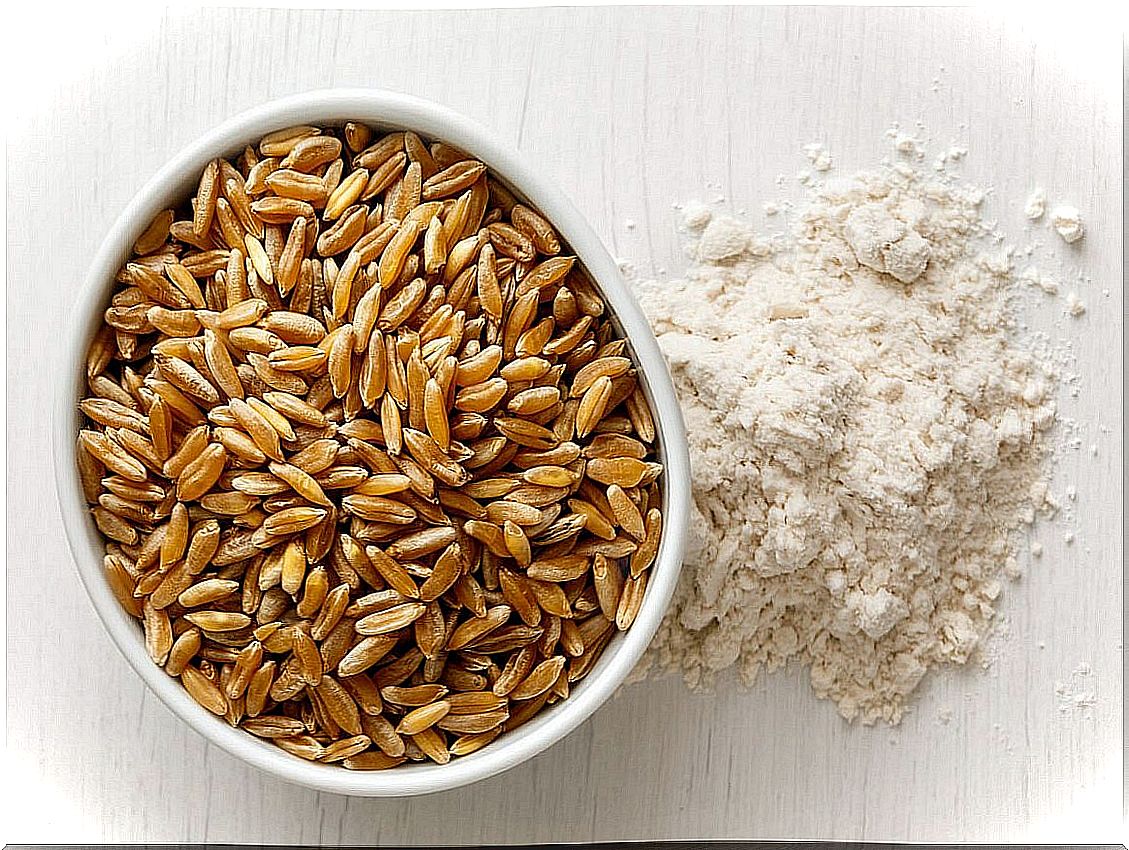

How to use kamut in the kitchen?
Kamut can be used like any cereal, that is, cooked with water. It is necessary to wash it and then place it in a pot to cook it.
After the minutes of cooking specified on the package, the kamut grains will be tender and ready to use as a side or as a main ingredient in salads.
On the other hand, it is possible to buy kamut flour for making pasta or breads. However, recipes with this ingredient have a certain complexity linked to its fermentation capacity.
Kamut: an increasingly used cereal
Due to its nutritional properties, kamut is gaining weight in Western cuisine. Its regular use allows it to provide health benefits, being this much more recommended than wheat, which stands out for its high level of refinement.
In addition, kamut has the advantage that it is very easy to prepare. It can serve as a side to almost any protein food, in the same way as rice or quinoa. In addition, it combines very well with vegetables. We recommend that you give it a try and start introducing it.