What Is Arterial Blood Gas And What Is It For?
An arterial blood gas is a medical technique that aims to measure the concentration of different gases and the pH in the blood. Blood is usually drawn from an artery, usually the radial artery in the wrist. The gases that are measured are almost always oxygen and carbon dioxide.
It is a test that is carried out as a diagnosis and that involves certain risks since there may be some complications. Therefore, doctors must assess and discuss whether it should be done or not.
How is an arterial blood gas performed?
This technique must be carried out by qualified personnel. They can be doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, or laboratory technicians.
To carry out this technique, the specialized person must pierce an artery with a needle and a syringe. As we have said before, it is usually the radial artery of the wrist, in order to extract a small volume of blood.
It can also be removed through the brachialis, which is located inside the arm at the elbow. However, before proceeding to draw the blood, we must make sure that the artery is supplying the blood well. To do this, the Allen test must be performed.
Allen test
This test lasts a few minutes and is used to check if there is a thrombotic problem in the hand or in the artery where the blood will be drawn. It consists of the following steps:
- The patient is asked to clench his fist with some force.
- Both the radial and ulnar arteries are compressed for a few seconds. This is to make the hand pale due to lack of blood.
- The specialized person must stop compressing the arteries and it should be observed that the hand returns to its natural color in about 15 seconds.
- If the hand color does not return to its natural color, this test should be performed elsewhere.
Once the test is finished, the area where the needle will be inserted is cleaned to avoid infection. A certain amount of blood is drawn into the syringe and pressure is applied to the artery to stop the bleeding.
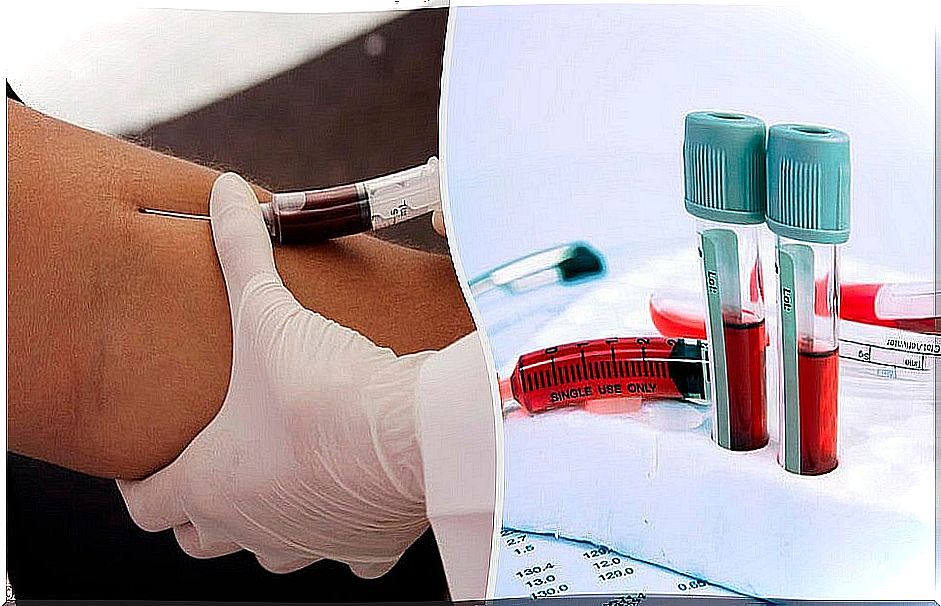
Once the blood is drawn, it is taken to the laboratory for the corresponding analysis. We explain it to you below.
What data does an arterial blood gas provide us?
At the beginning of the article we mentioned that oxygen and carbon dioxide levels are measured. However, through this analysis, we can also know the concentrations of both dissolved gases in the blood and those that are not soluble in it.
The concentrations of gases in the blood are a very useful data when evaluating the respiratory function of the body and its acid-base balance. The parameters that are measured in an arterial blood gas are the following:
- Arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- pH.
- Bicarbonate and lactate concentration.
- Hemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin.
- Electrolytes.
- Others.
Who should have an arterial blood gas test?
This type of blood test is usually done with the goal of analyzing lung function. Also for monitoring people who are undergoing oxygen treatment or respiratory therapy.
Arterial blood gases assesses the efficiency of the filtration of carbon dioxide in the lungs, as well as the circulation of oxygenated blood. When we breathe in oxygen, it passes from the lungs into the bloodstream.
On the contrary, when we exhale, it is the carbon dioxide that is released, also traveling through the blood. Therefore, these are the two most important factors that this analysis measures. Arterial blood gas is used mainly in people who suffer from some complication in lung function. Also in diabetic people.
Disorders detected by arterial blood gas
As we have seen, we breathe in oxygen, necessary for the functions of our cells, and we expel, as a waste substance, carbon dioxide. For this process to work correctly, the pH of our body must be within a specific range.
To control the body’s pH we have a balancing system that is made up of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate. Therefore, when the blood becomes acidic, that is, when its pH decreases, it is because the concentration of carbon dioxide increases. If, on the other hand, it becomes alkaline, it is due to the increase in bicarbonate.
We detect these imbalances thanks to arterial blood gases. Specifically there are 4:
- Metabolic acidosis : in this situation, the patient has a pH lower than normal, with a decrease in the concentration of bicarbonate. This situation may be due to consequences of suffering from diabetes mellitus or a kidney problem.
- Metabolic alkalosis : unlike the previous one, the pH is high and with it, the bicarbonate levels are high. One possible cause of this situation is prolonged vomiting.
- Respiratory alkalosis : due to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels in the blood and an increase in pH levels with increasing respiration. Hyperventilation, pain and certain diseases can be some of the causes of this situation.
- Respiratory acidosis : when we have difficulty breathing, carbon dioxide levels increase in the blood and the pH decreases. It can be due to chronic obstructive disease (COPD) or pneumonia.