Urinary Tract Infections In Children
Urinary tract infections can be serious and cause kidney damage. For this reason, it is essential to know your symptoms and see a doctor to start treatment early.
Urinary tract infections in children are quite common. This type of infection occurs when some bacteria manage to enter the urinary bladder and kidneys.
Thus, it is necessary to go to the doctor to start treatment as soon as possible. In the following lines we tell you what urinary tract infections are and what is their treatment.
Urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are defined as the presence or proliferation of microorganisms in the urination organs, with or without symptoms. Asymptomatic infection is called asymptomatic bacteriuria.
In this sense, as this study published in the journal Acta Médica Peruana points out , several types of urinary tract infections must be distinguished according to their location :
- Acute pyelonephritis (affects the kidney parenchyma).
- Lower urinary tract infection (cystitis).
For its part, the most common bacteria capable of developing urinary tract infections in children are P roteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacteria, Is treptococci Y Staphylococci . In newborns, they can also be presented by Li steria monocytogenes and Enterococcus , among the most frequent.
As we have said before, UTIs are frequent during childhood and, because they can be recurrent and develop long-term complications, it is essential to go to the pediatrician to start treatment as soon as possible.
Symptoms of urinary tract infections

The symptoms can be varied, depending on the age of the child. In fact, it is more difficult to detect in newborns or under six months. However, common symptoms to all are the presence of fever (usually higher than 37 ºC) and pain when urinating.
Thus, according to this article published in the MD Medical Journal , the most common symptoms are the following:
- Pain, burning, or stinging when urinating.
- Fever.
- Pain in the bladder area.
- Smelly, cloudy urine that may even contain blood.
- Irritability and vomiting.
- General malaise and chills.
- Constant urge to urinate, even when you urinate little at a time.
Precisely, in the case of acute pyelomyelitis, the symptoms are usually more severe. Indeed, in these cases severe fever symptoms appear, as well as tiredness, fatigue and inability to eat and vomiting.
On the other hand, as evidenced by this work carried out by professionals from the Ricardo Palma University of Lima, Peru, there are some risk factors associated with the appearance of urinary tract infections in children. Among the most common, we can highlight the following:
- Urinary tract problems (urinary tract obstructions, for example).
- Kidney malformations
- Vesicoureteral reflux, a disorder that causes urine to flow into the kidneys and ureters.
- Inadequate hygiene habits.
How is it diagnosed?
The doctor will proceed to a physical examination and, later, will indicate the performance of a urine analysis or culture. In general, the culture will allow the specialist to determine the type of infection and, therefore, choose the best treatment.
Moreover, ¿ how urine is collected for analysis depend on the age of the child? In older children, just ask them to urinate into a sterile container. However, in younger children who are still wearing diapers, it is normal to use a catheter to collect the sample.
How are UTIs treated?
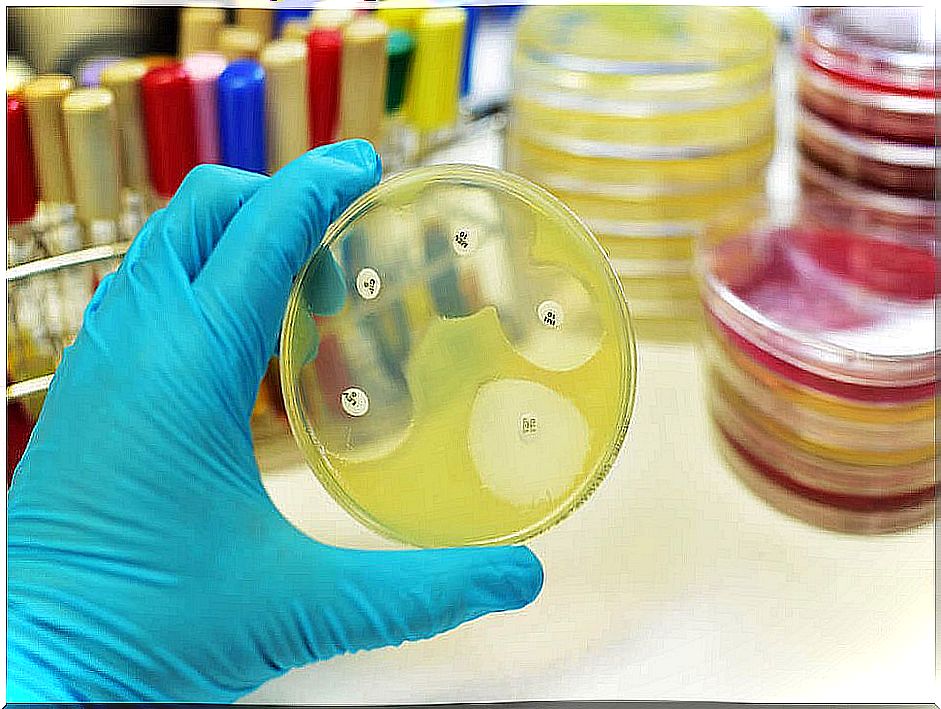
Treatment is with antibiotics. In fact, after administering them, the doctor may order a new urinalysis to confirm that the infection has disappeared. In this way, it is avoided that it can spread to other parts of the body or become recurrent.
However, in the most severe cases of urinary tract infections, the child may require hospitalization, especially if the child is younger than 6 months, if the infection has affected the kidney or the child is dehydrated.
Recommendations for parents
- First of all, with the appearance of the first symptoms, the child must be taken to the doctor for a diagnosis of the infection.
- Of course, after being diagnosed, you have to follow the specialist’s instructions and administer antibiotics in the amount, frequency and duration indicated.
- Likewise, it is necessary to keep track of the frequency of urination of children. In the event that they can express themselves, it is also necessary to ask them if they feel pain.
- On the other hand, the child must be encouraged to drink water to stay hydrated and avoid soft drinks, teas or infusions.
- Regarding prevention, in children who still use diapers, they must be changed frequently in order to maintain the hygiene of the urinary tract.
- In older children who already go to the bathroom alone, it is advisable to instill proper hygiene rules and habits. For example, teach girls to always wipe from front to back, as bacteria around the anus could enter the urinary tract.
- In addition, it is preferable to wear cotton underwear and avoid synthetic materials that hinder perspiration.
Ultimately, urinary tract infections are generally mild and can be easily treated with the use of antibiotics. If in doubt, consulting a pediatrician will always be the best option, as well as maintaining good hygiene habits in the little ones in the house.