Types Of Otitis
The different types of otitis occur mainly due to the action of bacteria. Most of the time this disease is cured quickly, without causing major consequences. However, there are cases in which the picture can become complicated and generate permanent sequelae.

The different types of otitis have in common the fact that they involve an ear infection. In turn, what differentiates them is the area of this organ in which they take place and the level of severity that each one implies. However, in most cases it is a benign disease.
The different types of otitis can affect people of any age and condition. However, they are more common during childhood. It is estimated that up to 60% of children under 4 years of age will suffer from otitis ; and up to 80% of children will have already suffered from the disease before the age of 6.
Although most types of otitis do not represent a serious health condition, in some cases they have significant consequences. Likewise, the use of antibiotics to control the disease causes resistance to the microorganisms that produce it to develop, giving rise to more complex pictures on some occasions.
What is and what are the types of otitis
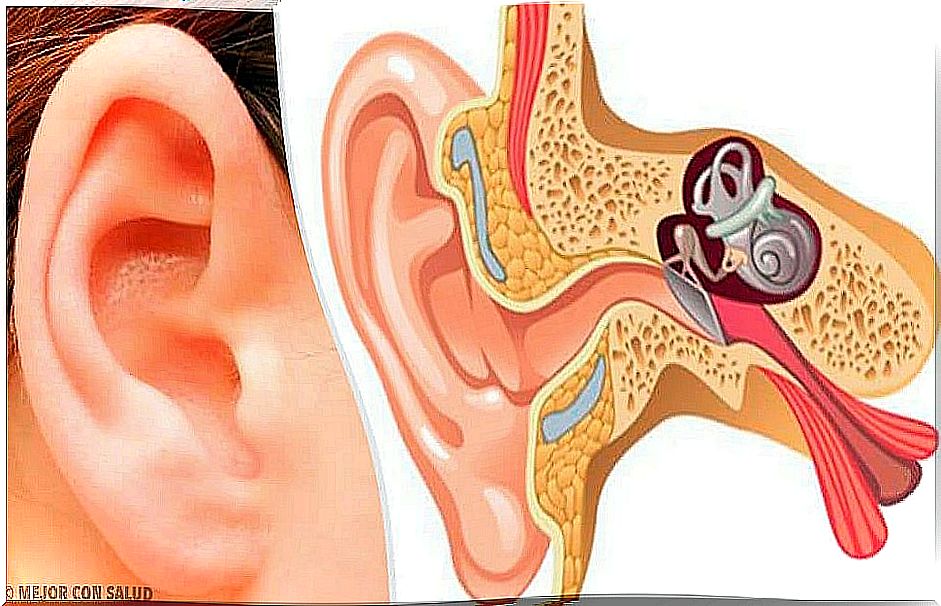
Otitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the ear. It is almost always caused by bacteria , particularly pneumococcus and moraxella. Only in a few cases is it caused by the action of viruses, although viral infections of the respiratory tract promote bacterial superinfection.
Influenza and parainfluenza viruses are often predisposing factors for contracting different types of otitis. Measles and chickenpox viruses are also sometimes present, although to a lesser extent. Polluted environments and the absence of breastfeeding are also risk factors.
From the point of view of its recurrence, otitis can be acute or chronic. Acute otitis occurs suddenly and for a short time, while chronic otitis occurs repeatedly, for long periods.
Depending on its location, the two basic types of otitis are external and medial ; each of them is divided into different subtypes:
External otitis
Otitis externa is an irritation, inflammation and / or infection of the outer part of the ear , as well as the external auditory canal. Generally, it is produced by fungi or bacteria, mainly by exposure to moisture. That is why it is also known as “swimmer’s ear” and occurs particularly in summer.
This type of otitis causes severe pain , inflammation, irritation, fever, and sometimes discharge, which can lead to temporary hearing loss. Otitis externa is slightly more common in adolescents and adult males. It usually heals in little more than a week and does not leave sequelae.
The types of external otitis are the following:
- Circumscribed or furunculosis : takes place when the hair follicle becomes infected. It is produced by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and usually arises from vigorous scratching, which causes small lesions.
- Bacterial diffuse : it is related to humidity and heat, which is why it occurs mainly in summer. The agent that mainly causes it is pseudomonas , which penetrates through contaminated water.
- Necrotizing or malignant : it is a serious modality that occurs mainly in older adults or people with immunity problems and diabetics. In this case, the infection spreads and causes osteomyelitis and / or cellulitis. Requires hospital management.
Otitis media
Otitis media occurs when the middle ear, located behind the eardrum, becomes infected. It should be noted that an ear infection can spread throughout the head, so it is essential to stop it in time.
There are three types of otitis media :
- Acute: it is the most common form of otitis media. It is acute because it is brief and painful. It occurs when the Eustachian Tube, which connects the ear and throat, becomes blocked due to colds, allergies, excess mucus, sinusitis, etc.
- Chronic: it is characterized because it persists or recurs and causes permanent damage to the ear. It occurs when the disease is resistant to treatment.
- Exudative or effusive : its main characteristic is that there is secretion of a seromucosal fluid inside the eardrum. There is a total blockage in the Eustachian tube and this facilitates the presence of this serous fluid.