Symptoms And Treatment Of A Malignant Lipoma
A lipoma is a lump made of fat cells that usually appears between the skin layer and the muscle layer. Although the most normal thing is that it does not evolve into a malignant lipoma (tumor), there are times when this does occur.
It usually forms in the areas under the skin of the shoulders, back or neck. Also, there are situations in which lipomas appear in different parts of the body, a condition called lipomatosis .
A lipoma is usually painless, it moves easily when pressed with your fingers. Being a lump, people can mistake it for cancer, however, a lipoma is not cancer, it is usually harmless and does not normally need treatment.
There are situations when this lump is bothersome, painful, and grows. In this situation it is recommended to undergo an operation and remove it. On the other hand, when the lipoma is malignant it is called liposarcoma . In this case, it is a type of cancer that develops in fat storage cells.
Soft tissue sarcoma is the strongest and most often develops in people 50 to 70 years of age. In this article, we will talk about the types of malignant lipomas, the symptoms that occur, how they are diagnosed and what is the treatment.
Type of malignant liposarcomas or lipomas
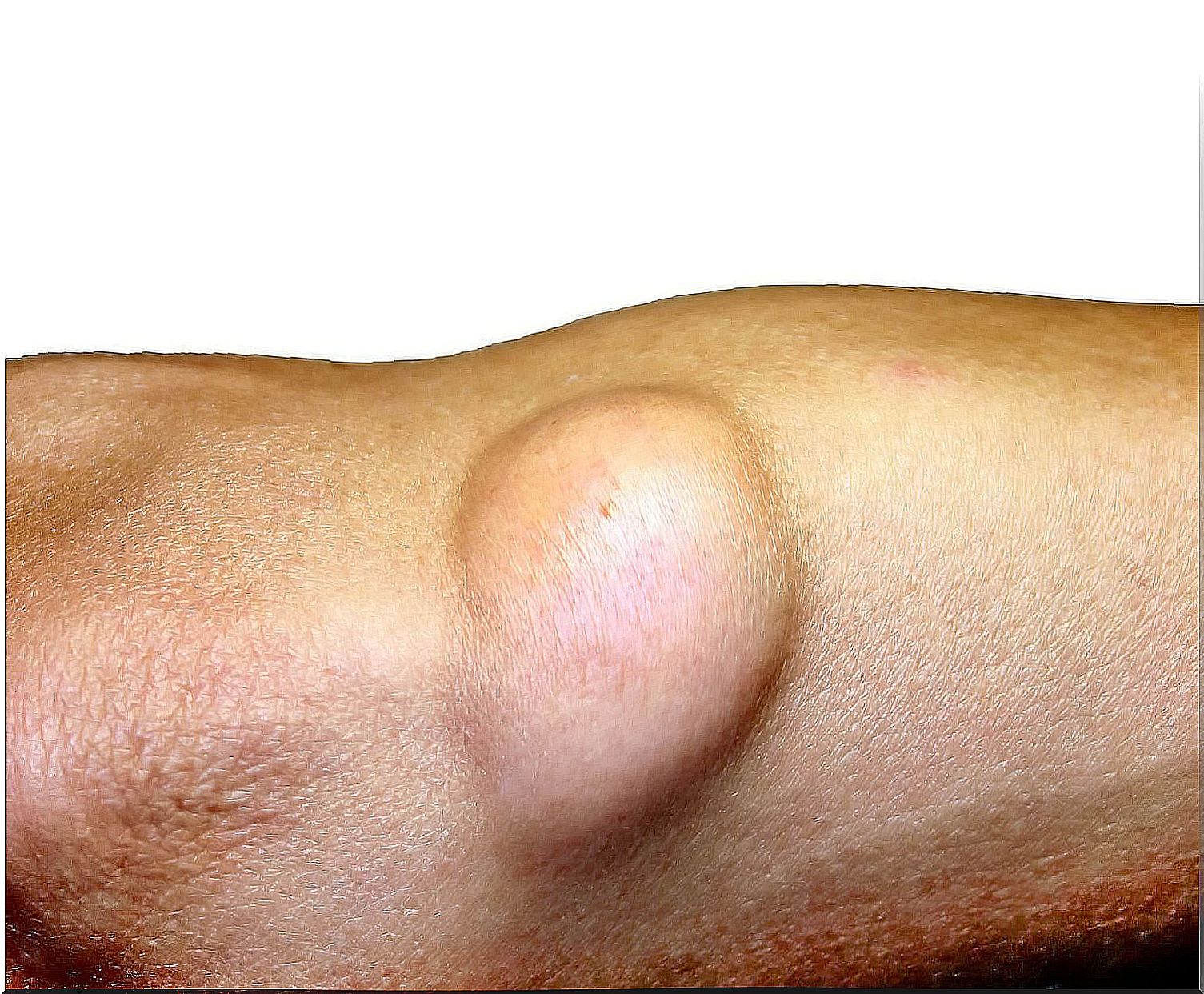
The reason why this type of cancer develops is not exactly known, but its appearance could have a genetic component. When a liposarcoma develops it can be a high-grade or low-grade tumor.
A low-grade malignant lipoma is one that grows slowly and does not spread to other areas of the body. As for high-grade tumors, they are larger and do spread normally to other cells.
The type of liposarcoma that will develop will depend on the type of cells that mutate and develop the tumor. We distinguish the following types of malignant lipomas:
- Well differentiated: it is the most common type. It is a tumor that is made up almost entirely of adipose tissue cells, adipocytes.
- Myxoid : after well-differentiated liposarcoma, it is the second most common. This type of tumor is usually located in the muscles of the leg.
- Dedifferentiated : formed by a fatty tumor and another without fat. This liposarcoma usually grows back after its removal and can spread to other areas of the body.
- Mixed : it is a tumor that is made up of more than one type of liposarcoma and usually grows in the abdomen.
- Pleomorphic : it is a rare type of tumor. It usually appears in the muscles of the legs and has little or no fat.
Signs and symptoms of a malignant lipoma
As has been said, liposarcomas are usually tumors that are painless and are normally slow growing. However, there are situations in which the tumor grows and can put some pressure on the nerves and blood vessels, triggering a painful situation.
Depending on the area where the tumor is, the symptoms will be different. Among them we can observe, if the tumor is located in an extremity, a reduction in its mobility.
In addition, the patient may experience pain and inflammation in the area where the tumor is located, pain in the chest and in the abdomen. Other characteristic symptoms of these tumors are the following:
- Weightloss.
- Bleeding in the stool
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Difficulty urinating and swallowing.
- Coughing and difficulty speaking and breathing.
How is a malignant lipoma diagnosed?
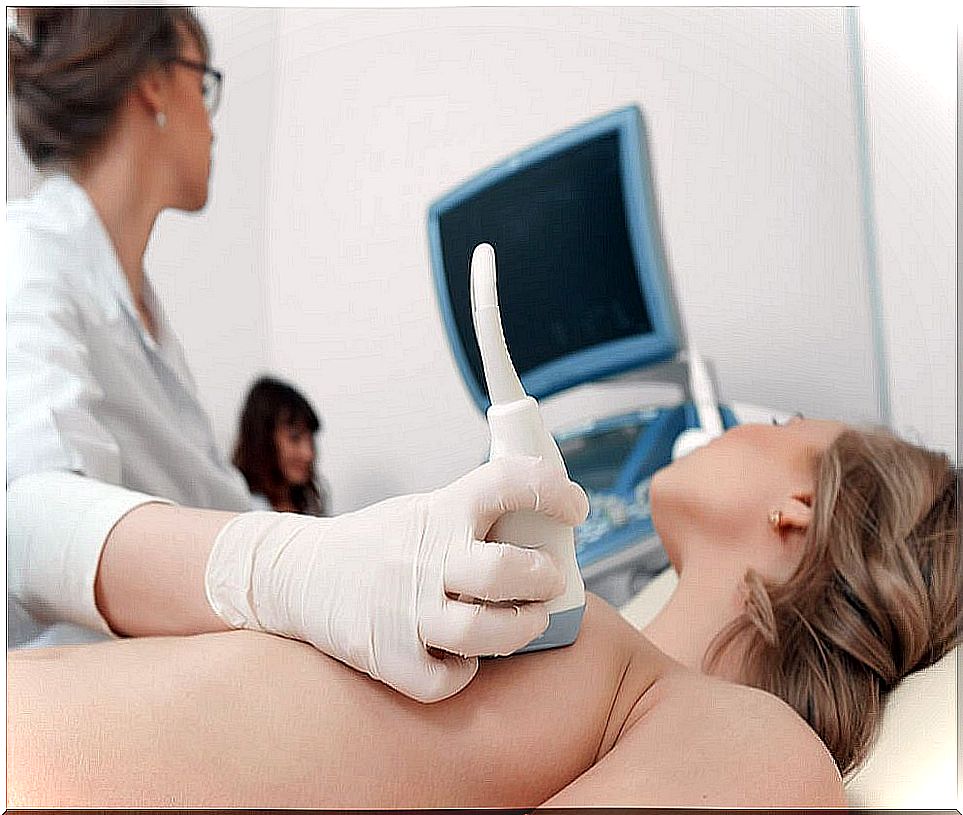
The first thing to do is a superficial palpation of the tumor. If it were a benign lipoma, in general, it would not require a special examination, since the general practitioner or dermatologist are able to differentiate it by touch and sight.
In the event that your diagnosis is in doubt, different techniques could be performed. First is the X-ray. This technique is used to take a picture of the tumor and the area around it. The x-ray shows whether the tumor has damaged the bones and whether it has spread to the lungs.
Computed tomography, also known as CT, is another technique used in the diagnosis of a malignant lipoma. It is a special X-ray machine. Another technique used is magnetic resonance imaging. This machine uses strong magnets and a computer to take pictures of the tumor and the area around it.
In addition, there is the positron emission tomography, which also serves to see if the patient has cancer and if it has spread. A dye is injected into the vein to help the cells show up more clearly.
Finally, there is the biopsy, in which a small sample of tissue is removed from the tumor for examination. With the examination it is possible to show if the tumor is finally a malignant lipoma and what type it is.
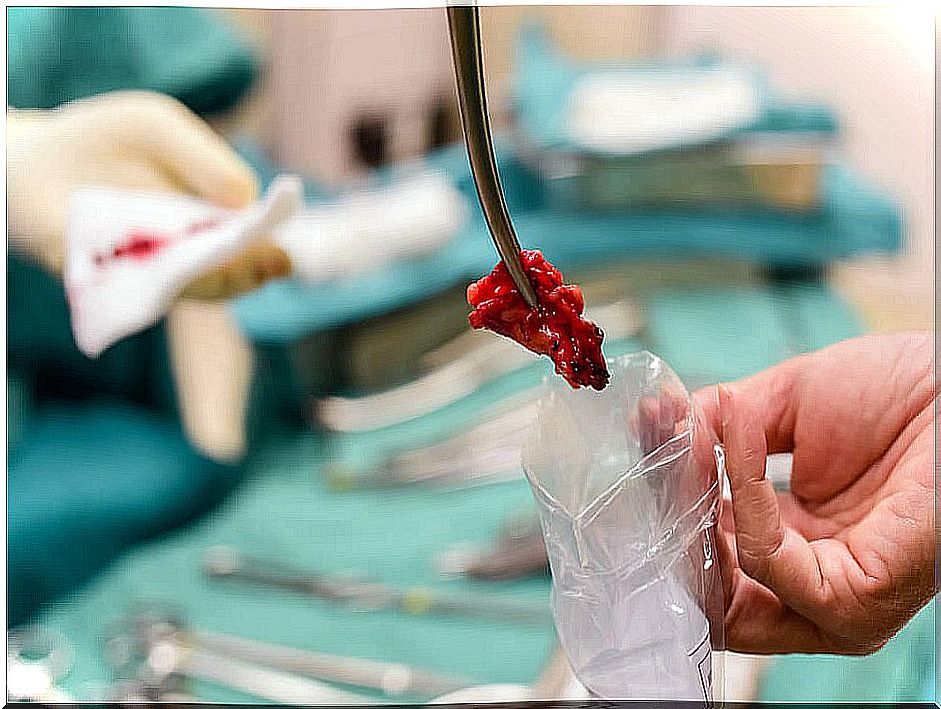
Malignant lipoma treatment
To treat liposarcomas we have the following procedures:
- Chemotherapy : This medication aims to kill the cells that make up the tumor. It is often used to shrink the tumor before surgery. It can also be given later to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Rays – Radiation kills cancer cells and prevents the spread of cancer.
- Surgery : this option is chosen in the event that it is necessary to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue.
Even with treatment, the malignant lipoma could come back, spread, or be life-threatening. For this reason, medical control will be essential for the patient.