Pinpoint Pupils Or Miosis: Why Does It Occur?
The word miosis is the medical term used to refer to the fact that the pupils become pinpoint. That is, it consists of the contraction of the pupil. Although it may seem irrelevant, pupil size can tell a lot about a person’s health.
This part of the eye reacts physiologically to changes in light, contracting or dilating. But in addition, its size varies when toxic substances are consumed or there is a brain injury. Therefore, we explain everything you need to know about miosis.
What is miosis?
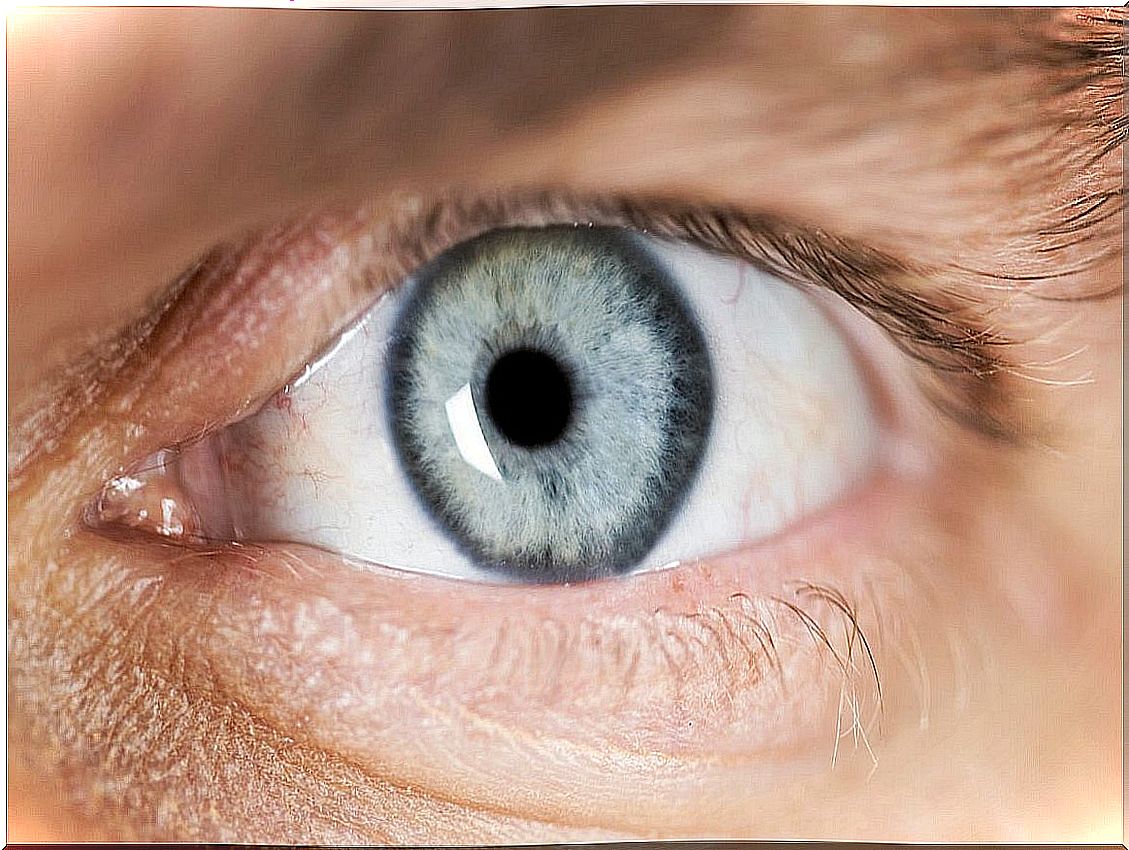
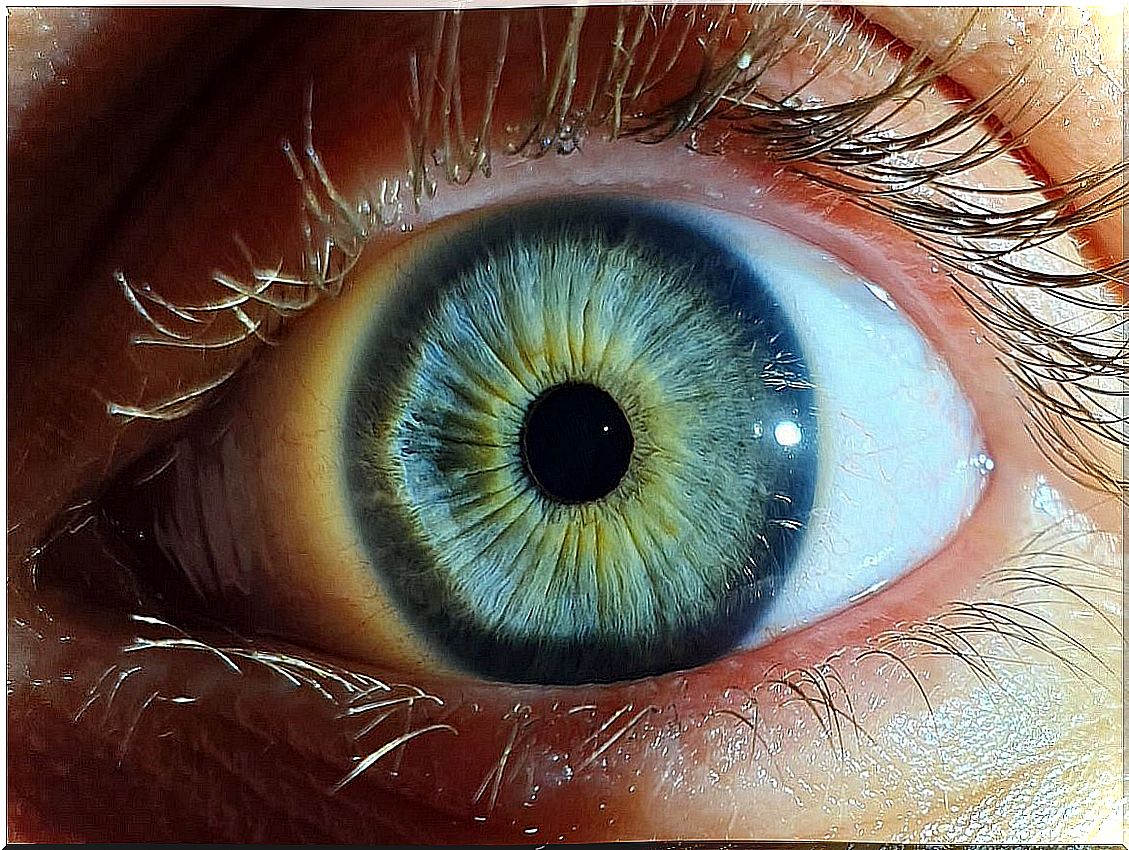
Miosis, as we have just pointed out, consists of the contraction of the pupil. The pupil is the hole in the center of the iris, that is, the dark part of the eye. It is responsible for controlling the amount of light that passes into the eyeball, towards the retina.
To do this, it can expand or contract, depending on how much light is in the environment. Thus, when the environment is dark, it dilates (which is called mydriasis ). On the contrary, when there is a lot of lighting, the pupil contracts. It is a normal and physiological reflex controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system.
These movements are carried out thanks to a muscle present in the eye called the ciliary muscle . When the pupil is dilated, the muscle that works is the dilator of the iris. In that case, the sympathetic nervous system is the one that coordinates the action.
Causes of pinpoint pupils or miosis
As we have explained, miosis is a physiological process that occurs in response to the amount of light. However, it is not the only situation that can cause this reaction. Certain substances or diseases can cause it, such as the ones we report below.
Opioid use
Opioids are substances derived from opium that act on the central nervous system. They are used both in the form of medications as well as recreational drugs. Some of them are fentanyl, morphine, heroin, and methadone.
Its action has a depressant mechanism in the nervous system. The pupils contract and hardly react to light stimuli. According to an article published in the Universidad Libre Seccional Barranquilla, opioid intoxication is characterized by miosis, respiratory and consciousness depression, among other signs.
Chemical poisoning
Besides opioids, there are many other chemicals that can cause this situation. In fact, several medications have miosis among their side effects. For example, some antipsychotics, such as haloperidol. The same is true for drugs used topically to treat glaucoma.
Horner syndrome and miosis
Horner syndrome is a set of symptoms that appear after a nerve injury. It causes the eyelid to be droopy and the pupil to present miosis. In addition, sweating on that side of the affected face is usually reduced.
According to an article published in the Acta Médica del Centro, one of the main causes of this syndrome is iatrogenesis. That is, it occurs as a result of a medical failure after surgeries on the face, for example, dental or therapeutic interventions applied for trigeminal neuralgia.
Cerebral haemorrhage
In some cases, depending on the area of the brain that is affected by brain bleeding, miosis may occur. For example, in cases where a stroke is very extensive or when the thalamus is involved.
Pancoast tumor
Pancoast tumor is a type of cancer that occurs in the lung. It can affect parts of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for producing the opposite effect to miosis (mydriasis). In this way, since the pupil cannot be dilated, it remains contracted as a result of this tumor.
How is the cause of miosis diagnosed?
To diagnose the cause of miosis, the basic thing is to observe the general condition of the patient. Many of the etiologies that produce the symptom, such as opioid intoxication or cerebral hemorrhage, are usually accompanied by an alteration in the level of consciousness.
If you are conscious, the ideal is to ask the person if they have used any drugs or drugs. In addition, it is necessary to observe how the pupils react to light stimuli. The doctor or nurse is in charge of studying different eye reflexes to check the neurological status.
Among them is the photomotor reflex, which is to observe if the pupil contracts more when exposed to light. Another is the consensus reflex, which confirms whether the pupil of the other eye (the one that is not being illuminated) is also contracting. This shows whether the injury is in one of the peripheral nerves or in the upper brain area.
A physiological reflex
Miosis is a physiological mechanism that occurs in response to light. However, it can also be secondary to neurological damage or intoxication by certain substances.
Therefore, it is an essential part of the medical examination and provides a lot of information about the patient’s condition. When the sign is persistent, then we must doubt an underlying pathological process.