How To Raise Children With Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes constitutes approximately 13% of the total cases of diabetes in Spain. It currently affects 29,000 children and 1,100 new cases arise each year.
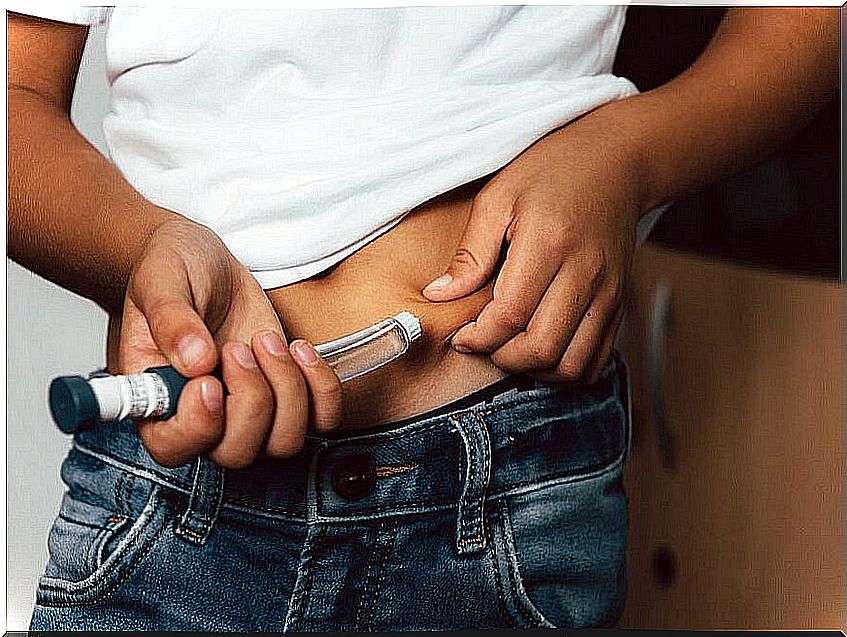
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic disease that, properly controlled, does not have to reduce the quality of life of people who suffer from it. However, l children with diabetes will require a series of specific care.
Next, we are going to explain what type 1 diabetes is and we are going to give some tips for raising children with this condition.
What is type 1 diabetes?

It represents approximately 10% of diabetes cases and its maximum incidence occurs between 10-15 years. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas loses its ability to make insulin because the immune system attacks and destroys its beta cells.
This hormone is necessary to allow glucose to enter the cells to produce energy, therefore, it is of vital importance to counteract its deficit.
Currently, type 1 diabetes has no cure. His treatment focuses on controlling blood glucose levels through insulin administration and a healthy lifestyle. All of this is evidenced by this information provided by KidsHealth .
The exact causes that trigger this disease are not known, but it is believed that factors such as genetics and certain viruses can contribute to the appearance of it. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or pre-adolescence, it can also begin in adulthood.
Tips for Raising Children With Type 1 Diabetes

Next, we are going to present a series of general recommendations so that both the family and the child can cope with diabetes and that it does not compromise their quality of life.
1. Knowledge of the disease
Once the child receives the diagnosis, it is very important that they know the basic aspects of the disease and carry out a normalization process in their closest environment, so that they adapt and learn to live with it.
Family members and teachers must know the guidelines for action and participate in the pharmacological and emotional control of the child.
2. Feeding guidelines for children with diabetes
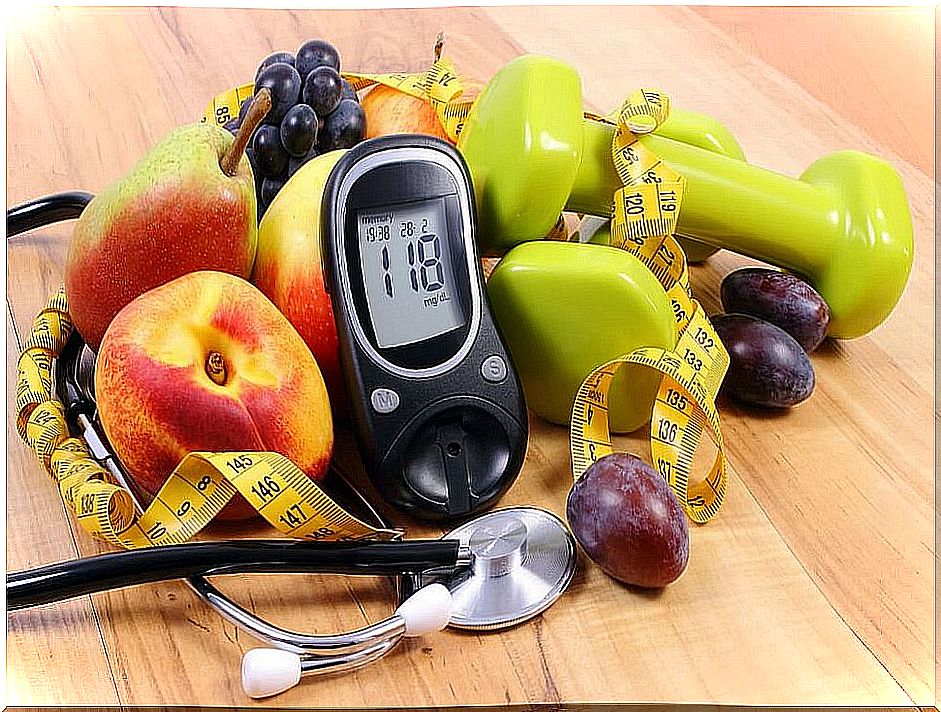
Food is key to the treatment of children with diabetes and it is very important that, both at home and at school, the child is controlled and follows appropriate schedules. The main recommendations to be taken into account are the following, taking as a reference this study published in the Journal of the Bolivarian Society of Pediatrics :
- Balanced diet : it is necessary to control the amount of fat ingested by the child, since this reduces the effect of insulin and favors the appearance of overweight. Fruits and vegetables, as well as high-quality proteins and complex carbohydrates, should be included in all meals.
- Limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates : It is essential to restrict your intake to avoid rapid rises in blood glucose. These foods include added sugars, industrial pastries, juices, honey, or cookies.
- Food at school. Teachers have to provide parents with weekly menus. In addition, if the child is very young, educators have to watch out for him to have a second breakfast or lunch so that the blood sugar levels remain stable.
3. Control of drug treatment
Children with type 1 diabetes have to inject insulin several times a day : fast-acting before each meal and slow-acting once or twice a day.
Try to administer the drug in a relaxed environment and preferably at home. Teachers need to know the procedure in case the child is too young and needs help giving the injections. And this is evidenced by this practical guide for diabetes in children.
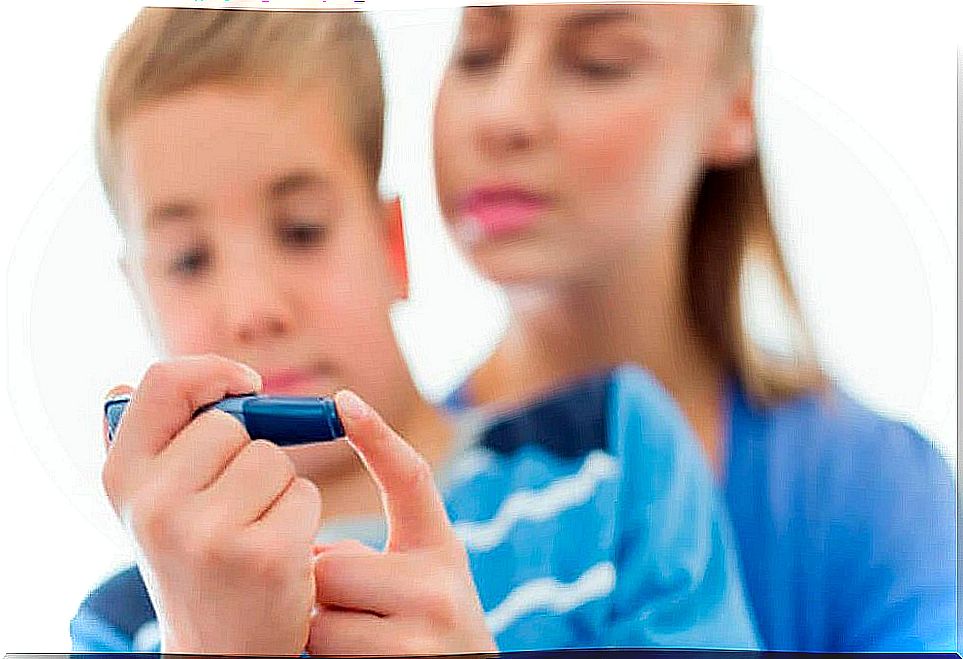
4. Control of blood glucose in children with diabetes
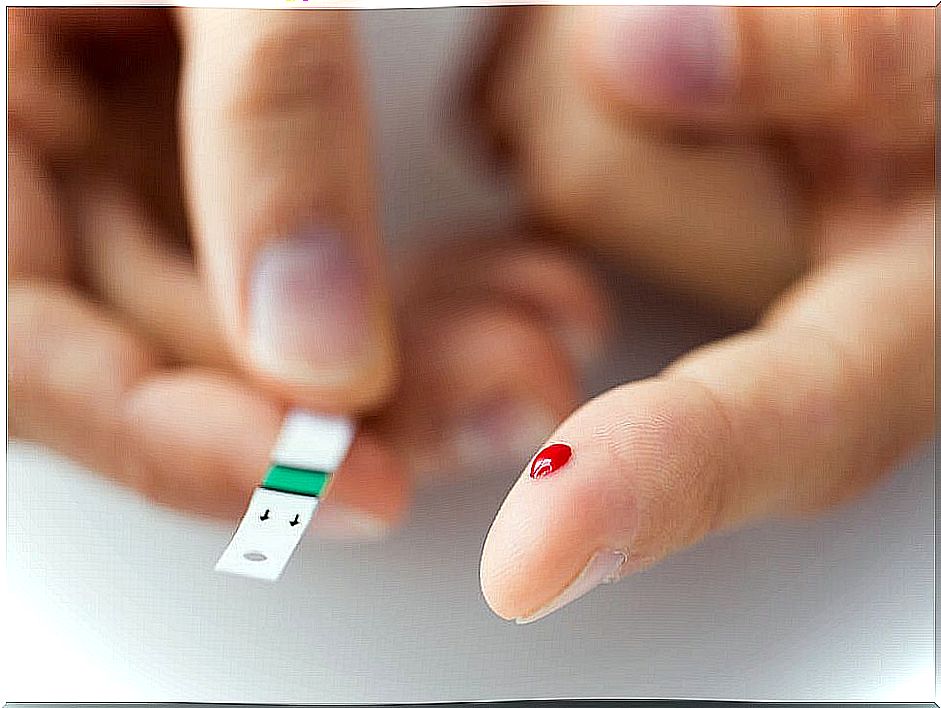
Children with diabetes need regular checks, with a small prick of the index finger, to know their blood glucose levels. At school, the little one should be able to do them in class or have a place where they feel comfortable to do it.
6. Exercise
Children with diabetes can perform the same physical activities as other children their age, as long as a series of recommendations are followed:
- Measurement of blood sugar before and after exercise to be able to adapt the diet if necessary.
- Parents or teachers present during physical activity must have quick access to carbohydrate-rich foods in the event of a drop in blood glucose (hypoglycemia).
In short, the current tools in the control of type 1 diabetes allow a good quality of life for these patients. In the case of children, it is necessary to know the characteristics of the disease by parents and teachers to ensure good glycemic control.