Atelectasis: Symptoms And Causes
Atelectasis can be caused by trauma or by having undergone general anesthesia, among other causes.
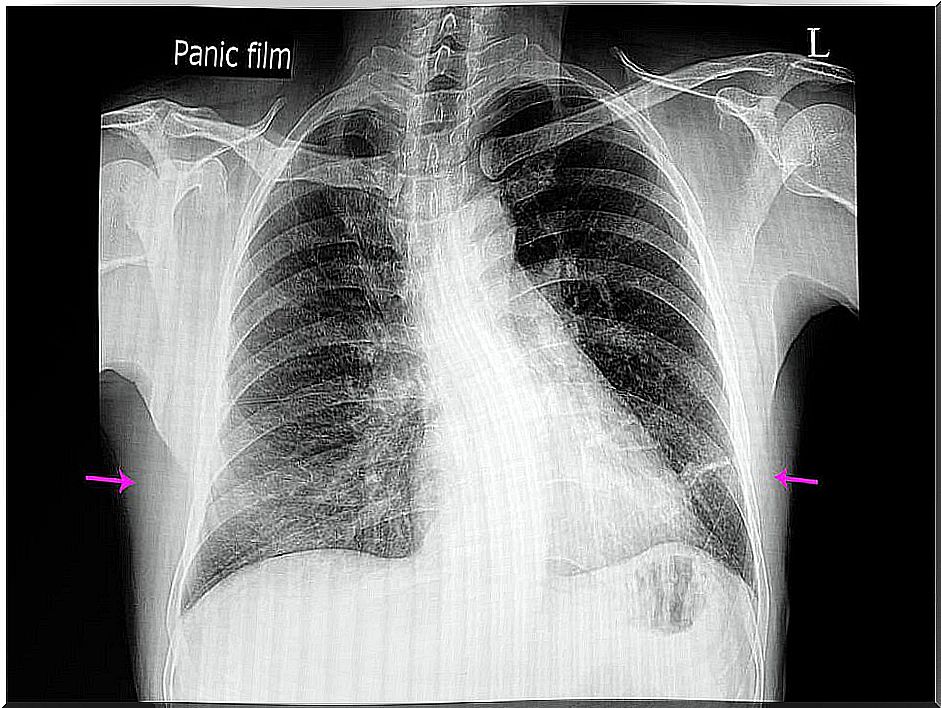
The word atelectasis comes from atele-vs (incomplete) and ecstasy (expansion). It is a disorder in which part of the lung is deprived of air and collapses.
It can be of the whole lung or of a part (lobe). Generally, it is caused by an obstruction of the airways or by pressure on the outside of the lung. As a result, the alveoli deflate or fill with fluid.
It is a frequent complication of certain respiratory problems. For example, it can occur in cystic fibrosis, lung tumors, thoracic surgeries, and so on. Even atelectasis can occur after inhaling a foreign object.
Atelectasis can cause breathing difficulties. In this article we explain what it consists of. Also what are its symptoms and causes. Keep reading!
Symptoms of atelectasis
It is important to differentiate it from pneumothorax. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks out of the lung. Atelectasis is the decrease of air in the lungs with loss of volume of the affected lung, while pneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleura.
Atelectasis may not cause any obvious symptoms. When it affects a small part of the lung, or if it develops slowly, the symptoms may be unnoticeable. On the contrary, if it affects a large number of alveoli, the symptoms can be severe. It also happens when it starts quickly. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing.
- Shallow, shallow breathing.
- Cough.
- Wheezing
- Chest pain: occurs mainly when the cause is trauma or pneumonia.
- Tachycardia and hypotension.
- Cyanosis: it is due to hypoxemia. It is the result of the decrease in gas exchange.
When breathing becomes progressively difficult, it is essential to consult a doctor.
Causes of atelectasis
Atelectasis, in the first place, can be caused by an obstruction of the bronchi or bronchioles. It can also be due to pressure on the outside of the lung.
The general anesthetic is a common cause. This is because the regular rhythm of breathing changes. In this way, it affects the exchange of pulmonary gases. Therefore, anesthesia can cause the alveoli to deflate. Almost all people who have major surgery develop some degree of atelectasis.
To mention the most common causes of atelectasis, we distinguish between obstructive and non-obstructive atelectasis.
Causes of obstructive atelectasis
- Foreign bodies: it is common in children. They tend to inhale small objects, such as parts of toys.
- Mucus plug: is a collection of mucus in the airways. It usually occurs in surgeries, as they make it difficult to expel the mucus by not being able to cough. It is also because many medications used decrease the depth of breathing. Thus, the mucus accumulates. In people with cystic fibrosis or asthma, mucus plugs are common.
- Tumors: a tumor in the tubes causes them to narrow. Thus, it enables obstruction.
Causes of non-obstructive atelectasis
Possible causes include:
- Trauma: when it occurs, pain reduces the depth of breaths. It can cause compression of the lungs.
- Pleural effusion : consists of the accumulation of fluid between the lung pleura and the interior of the chest wall.
- Pneumonia.
- Scars in the lung tissue. Injury, lung disease, or surgery can cause scarring.
Diagnosis
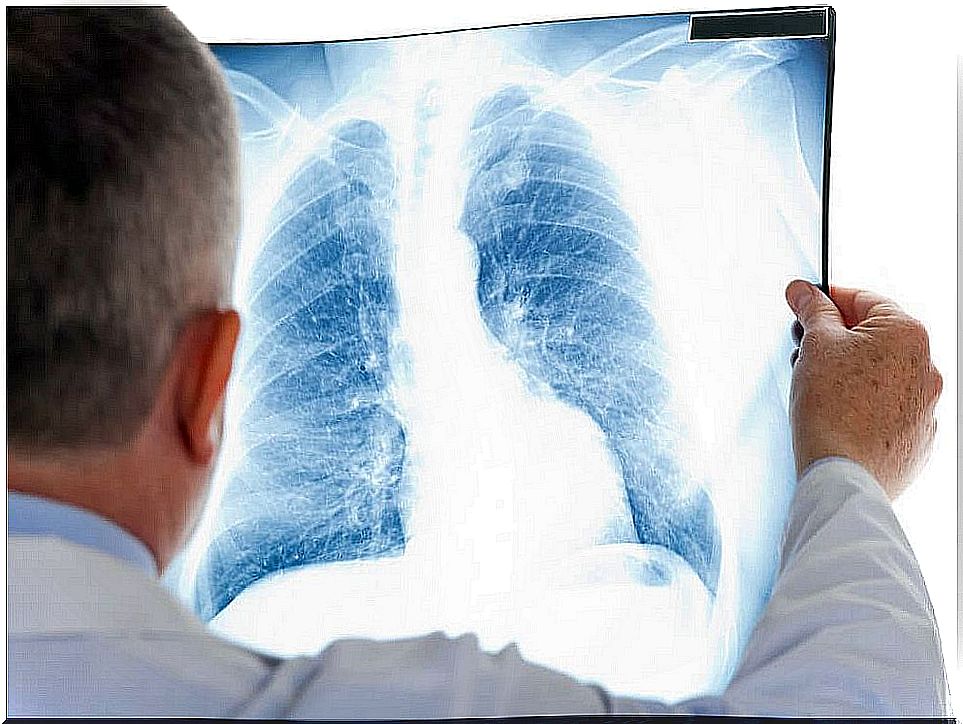
To diagnose atelectasis, an adequate clinical examination and radiography are usually sufficient. Still, a number of techniques can be used to confirm the diagnosis or measure severity.
These include computed tomography, bronchoscopy, ultrasound, and oximetry. In fact, bronchoscopy makes it possible to observe obstructions, and even remove the blockage.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause. In fact, mild atelectasis can go away without treatment. Therefore, we list the main ones:
- Remove obstruction by bronchoscopy
- Percuss the chest to loosen the mucus plugs.
- Inhaled medicines to open the airways. Medications are also used to thin the mucus.
- Treat the tumor if there is one
In some cases, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is used. It is useful in people who cannot cough and suffer hypoxemia, usually after surgery.
Conclution
Atelectasis is a disorder that can go unnoticed. However, it can be a serious problem, or be the result of an underlying disorder. Therefore, it is necessary to know its causes and symptoms to establish the best treatment, if necessary. Before any respiratory difficulty, it is necessary to go to the doctor.